Given a sorted linked list write a program to insert data into it’s correct position.
For example consider the following linked list
1 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5
Inserting 2 should change the list to
1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5
Inserting 0 should change it to
0 -> 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 ->5
Inserting 6 should change it to
0 -> 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 -> 6.
The three examples indicate three different cases to be considered while inserting into a sorted linked list.
Case 1: List can be empty or new element is added as the first element
Case 2: New element can be inserted anywhere in the middle of the linked list
Case 3: New element is added as the last element.
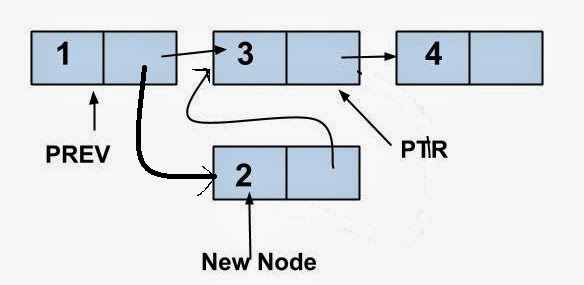
The following diagram illustrates the insert process.
In the following C++ program case 1 is handled in one block and case 2 and 3 are handled in the last block.