Given a binary tree, write a program to count the number of leaf nodes. A leaf node is a node which does not have left and right children.
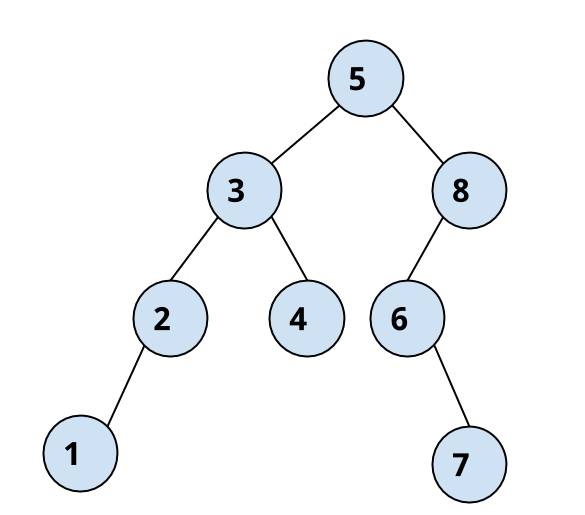
For example consider the following binary tree.
For example consider the following binary tree.
It has 3 leaf nodes namely 1, 4 and 7.
The solution is simple. The number of leaf nodes of a binary tree rooted at R is the sum of leaf nodes in the left and sub trees. Using this property we can devise a simple recursive solution.
This can also be solved using iterative solution by traversing the binary tree using BFS (Breadth First Search) traversal.
The following C++ program shows both recursive and iterative implementations.
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| #include <iostream> | |
| #include <queue> | |
| using namespace std; | |
| struct TreeNode | |
| { | |
| int val; | |
| TreeNode *left, *right; | |
| TreeNode(int v):val(v),left(NULL), right(NULL) | |
| { | |
| } | |
| }; | |
| //Binary search tree insert procedure for creating binary tree to test | |
| TreeNode* insert(TreeNode * root, int data) | |
| { | |
| if( root == NULL ) | |
| { | |
| root = new TreeNode(data); | |
| return root; | |
| } | |
| if( data < root->val ) | |
| root->left = insert( root->left, data ); | |
| else | |
| root->right = insert( root->right, data ); | |
| return root; | |
| } | |
| int leafNodes(TreeNode *root ) | |
| { | |
| if( root == NULL ) | |
| return 0; | |
| if( root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL ) | |
| return 1; | |
| return leafNodes( root->left ) + leafNodes(root->right); | |
| } | |
| int leafNodesIterative(TreeNode *root ) | |
| { | |
| if( root == NULL ) | |
| return 0; | |
| int count = 0; | |
| queue<TreeNode*> Q; | |
| Q.push( root ); | |
| while ( !Q.empty() ) | |
| { | |
| TreeNode * temp = Q.front(); | |
| Q.pop(); | |
| if( temp->left == NULL && temp->right == NULL ) | |
| count++; | |
| if( temp->left != NULL ) | |
| Q.push( temp->left ); | |
| if( temp->right != NULL ) | |
| Q.push( temp->right ); | |
| } | |
| return count; | |
| } | |
| void TestCase1() | |
| { | |
| TreeNode * root = NULL; | |
| root = insert( root, 2); | |
| root = insert( root, 1); | |
| root = insert( root, 3); | |
| cout << leafNodes( root ) << endl; | |
| } | |
| void TestCase2() | |
| { | |
| //binary tree which contains only right children | |
| TreeNode * root = NULL; | |
| root = insert( root, 1); | |
| root = insert( root, 2); | |
| root = insert( root, 3); | |
| cout << leafNodes( root ) << endl; | |
| } | |
| void TestCase3() | |
| { | |
| //binary tree which contains only left children | |
| TreeNode * root = NULL; | |
| root = insert( root, 3); | |
| root = insert( root, 2); | |
| root = insert( root, 1); | |
| cout << leafNodes( root ) << endl; | |
| } | |
| void TestCase4() | |
| { | |
| //Test with empty tree | |
| TreeNode * root = NULL; | |
| cout << leafNodes( root ) << endl; | |
| } | |
| void TestCase5() | |
| { | |
| //test with single node | |
| TreeNode * root = NULL; | |
| root = insert( root, 3); | |
| cout << leafNodes( root ) << endl; | |
| } | |
| void TestCase6() | |
| { | |
| TreeNode * root = NULL; | |
| root = insert( root, 5); | |
| root = insert( root, 3); | |
| root = insert( root, 2); | |
| root = insert( root, 4); | |
| root = insert( root, 7); | |
| root = insert( root, 6); | |
| root = insert( root, 8); | |
| cout << leafNodes( root ) << endl; | |
| } | |
| int main() | |
| { | |
| TestCase1(); | |
| TestCase2(); | |
| TestCase3(); | |
| TestCase4(); | |
| TestCase5(); | |
| TestCase6(); | |
| return 0; | |
| } |
 by
by