Traversal algorithms of non-linear data structures like trees are designed to visit/print all the elements in that structure.
There are three main traversals of the binary tree. Namely
- In-order traversal
- Post-order traversal
- Pre-order traversal
In addition to these, there are inverses of the above algorithms, and there is a level order traversal.
In this post we will see the three main traversal algorithms mentioned above. All of these are defined as recursive algorithms.
In In-order traversal, we first visit the left sub-tree, then root, and then the right sub-tree.
In Post-order traversal, we first visit the left sub-tree, then the right sub-tree, and then the root.
In Pre-order traversal, We first visit the root, then visit the left sub-tree and then visit the right sub-tree.
For example consider the simple 3 node binary tree
In-order traversal: B A C
Post-order traversal: B C A
Pre-order traversal: A B C
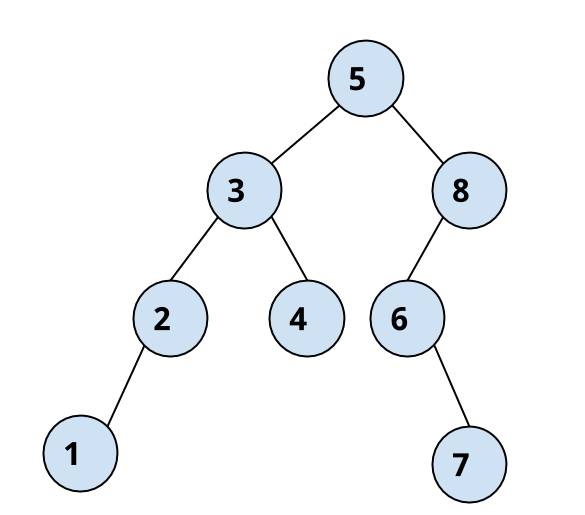
To consider a bigger example, take the following binary search tree and it’s traversal sequences for the three algorithms.
In-order: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Post-order: 1 2 4 3 7 6 8 5
Pre-order: 5 3 2 1 4 8 6 7
The in-order traversal of the binary search tree always produces the sorted order of it’s elements.
Here is the C++ code for all the traversals.
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| #include <iostream> | |
| using namespace std; | |
| class BSTNode | |
| { | |
| int data; | |
| BSTNode *left; | |
| BSTNode *right; | |
| public: | |
| //single param constructor | |
| BSTNode(int d):data(d), left(NULL), right(NULL) | |
| { | |
| } | |
| BSTNode(int d, BSTNode *l, BSTNode *r):data(d), left(l), right(r) | |
| { | |
| } | |
| int getData() | |
| { | |
| return data; | |
| } | |
| void setData(int d) | |
| { | |
| data = d; | |
| } | |
| BSTNode* getLeft() | |
| { | |
| return left; | |
| } | |
| void setLeft(BSTNode *l) | |
| { | |
| left = l; | |
| } | |
| BSTNode* getRight() | |
| { | |
| return right; | |
| } | |
| void setRight(BSTNode *r) | |
| { | |
| right = r; | |
| } | |
| }; | |
| class BinarySearchTree | |
| { | |
| BSTNode * root; | |
| public: | |
| BinarySearchTree():root(NULL) | |
| { | |
| } | |
| BSTNode * getRoot() | |
| { | |
| return root; | |
| } | |
| bool insert(int d) | |
| { | |
| if( root == NULL ) // if tree is empty | |
| { | |
| root = new BSTNode(d); | |
| return true; | |
| } | |
| else | |
| { | |
| BSTNode *ptr = root; | |
| BSTNode *prev = NULL; | |
| while( ptr != NULL ) | |
| { | |
| prev = ptr; | |
| if( ptr->getData() == d )//no duplicates allowed in BST | |
| return false; | |
| else if( ptr->getData() < d ) | |
| { | |
| ptr = ptr->getRight(); | |
| } | |
| else | |
| { | |
| ptr = ptr->getLeft(); | |
| } | |
| } | |
| if( prev->getData() < d ) //to be added as right child? | |
| prev->setRight( new BSTNode(d) ); | |
| else | |
| prev->setLeft( new BSTNode(d) ); | |
| return true; | |
| } | |
| } | |
| void inorder(BSTNode *root) | |
| { | |
| if( root ) | |
| { | |
| inorder( root->getLeft() ); | |
| cout<< root->getData() << " "; | |
| inorder( root->getRight() ); | |
| } | |
| } | |
| void preorder(BSTNode *root) | |
| { | |
| if( root ) | |
| { | |
| cout<< root->getData() << " "; | |
| preorder( root->getLeft() ); | |
| preorder( root->getRight() ); | |
| } | |
| } | |
| void postorder(BSTNode *root) | |
| { | |
| if( root ) | |
| { | |
| postorder( root->getLeft() ); | |
| postorder( root->getRight() ); | |
| cout<< root->getData() << " "; | |
| } | |
| } | |
| }; | |
| int main() | |
| { | |
| BinarySearchTree *bst = new BinarySearchTree(); | |
| bst->insert(5); | |
| bst->insert(3); | |
| bst->insert(8); | |
| bst->insert(4); | |
| bst->insert(9); | |
| bst->insert(1); | |
| bst->insert(10); | |
| bst->insert(2); | |
| bst->insert(6); | |
| bst->insert(7); | |
| bst->inorder( bst->getRoot() ); | |
| cout << endl; | |
| bst->preorder( bst->getRoot() ); | |
| cout << endl; | |
| bst->postorder( bst->getRoot() ); | |
| cout << endl; | |
| return 0; | |
| } |

 by
by